The varieties of hallucinogenic mushrooms have sparked curiosity and fascination for centuries. From ancient rituals in different cultures to modern scientific research, these mushroom species have been linked to both the spiritual and therapeutic worlds.
Their diversity is remarkable: we are not talking about a single type of mushroom, but a wide range of species with very different characteristics, potencies, and effects. Why are there so many, and what makes them special? Learning about them in depth not only helps us understand their role in human history, but also explains the growing interest they generate today in medicine, psychology, and contemporary culture.
What are hallucinogenic mushrooms and why are there so many varieties?
Hallucinogenic mushrooms are fungi that contain psychoactive compounds, the most well-known being psilocybin. Once ingested, this substance converts into psilocin, which is responsible for changes in perception, shifts in mood, and mystical or introspective experiences.
When we talk about hallucinogenic mushroom varieties, we refer to the wide diversity of species that exist in nature. More than 200 different types have been identified worldwide, each with its own traits in terms of potency, duration of effects, and growth environment. Some thrive in tropical climates, while others grow in temperate or humid regions, demonstrating the impressive adaptability of these fungi.

Main hallucinogenic mushroom varieties
When we discuss types of hallucinogenic mushrooms, we enter an immense world where nature has shaped species with different strengths, habitats, and cultural uses. Some are easy to find in forests or meadows, while others have become favorites for laboratory cultivation. Below, we explore the most representative ones, notable both for their history and the effects they produce.
Psilocybe cubensis
Psilocybe cubensis is without a doubt the most famous and widely cultivated variety in the world. Its popularity comes from being relatively easy to grow, making it the first choice for beginners in mycology. Within this species are popular strains such as the Golden Teacher and Mexican magic mushrooms. Its effects are usually visual, with a sense of euphoria and spiritual connection, making it especially attractive for controlled psychedelic experiences.
Psilocybe mexicana
Psilocybe mexicana holds a very special historical place, as it was used for centuries in sacred rituals by indigenous cultures of Mexico. Its strength is more moderate than other species, making it an excellent option for beginners or for those seeking a gentler, more contemplative experience. It is also closely related to magic truffles, since the sclerotia sold legally in some countries today come from this species. A mushroom full of symbolism and tradition.
Psilocybe semilanceata
Known as the Liberty Cap, Psilocybe semilanceata is one of the most widespread varieties in Europe. It grows naturally in damp meadows and temperate climates, which explains its broad distribution. Despite its small size, it is surprisingly potent, sometimes surpassing larger species in psilocybin concentration. However, it is difficult to cultivate in controlled environments, so it is mostly found in the wild.
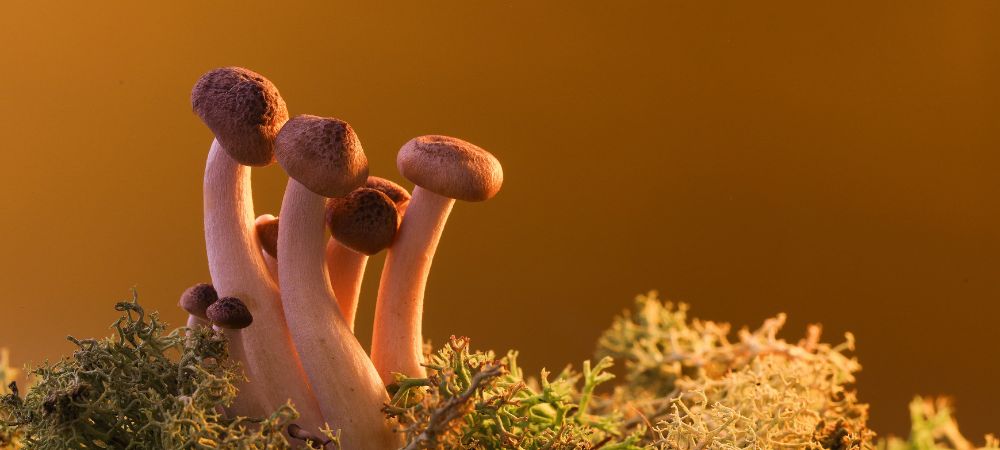

Psilocybe tampanensis
Psilocybe tampanensis is famous for producing the so-called “philosopher’s stones” or sclerotia, underground structures rich in psilocybin. Its effects are associated with deep, introspective, and sometimes mystical experiences. For this reason, it has been valued in therapeutic and spiritual settings, where the goal is self-exploration. Although less common, it holds a special place among enthusiasts and experts seeking a more reflective journey.
Other notable species
In addition to the ones mentioned above, there are many other hallucinogenic mushroom varieties worth mentioning.
- Psilocybe azurescens is considered one of the most potent in the world, capable of inducing intense visions even at small doses.
- Psilocybe cyanescens, known as “wavy caps” due to the marks it leaves when handled, grows on decaying wood and is recognized for its strong visual effects.
- Another species is Panaeolus cyanescens, also called Copelandia mushroom, which is known for its high potency and fast onset of effects. These species further enrich the vast mycological landscape.
[ppgbo products=”2680,2674,8015″ language=”en”]
Factors that differentiate varieties of hallucinogenic mushrooms
When we talk about hallucinogenic mushroom varieties, it’s not enough to simply say they all produce psilocybin. Each species has unique traits that shape the experience and influence their popularity among psychonauts and mycologists. From potency to habitat, there are several key factors that set them apart.
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Psilocybin and psilocin content | Some species, like Psilocybe azurescens, contain very high levels, while others offer a milder and slower effect. This directly impacts the intensity of the trip and the type of user they appeal to. |
| Effects | Some mushrooms induce strong visual and colorful experiences, others invite deep introspection and meditation, and some generate an expansive body energy. That’s why certain varieties are better suited for spiritual rituals, while others fit recreational or therapeutic contexts. |
| Growth environment | Some species grow naturally in damp meadows or temperate forests, while others have been adapted to indoor cultivation thanks to kits and modern techniques. This makes certain varieties highly accessible, while others remain rare and sought after by collectors. |
Understanding these nuances not only highlights the richness of the fungal world, but also explains why the diversity of hallucinogenic mushroom varieties continues to fascinate both researchers and explorers of consciousness.
Traditional and modern uses of hallucinogenic mushrooms
Hallucinogenic mushrooms have accompanied humanity for centuries, always linked to spiritual, healing, and more recently, scientific experiences. Each mushroom variety offers unique nuances, but they all share a common foundation: their ability to alter perception and open doors to new states of consciousness.
In shamanic practices and ancestral rituals, indigenous peoples of Mexico, Central America, and other regions used species like Psilocybe mexicana in sacred ceremonies. They were consumed to connect with the divine, seek spiritual answers, and heal at the community level.
Today, modern therapeutic research has reignited interest in these species. Multiple clinical studies are exploring the potential of psilocybin to treat treatment-resistant depression, anxiety in patients with severe illnesses, and even addictions to alcohol or nicotine.
Recreational and cultural use has also expanded in recent decades, especially in urban settings and festivals. Many users value hallucinogenic mushrooms as a tool to explore altered states of consciousness, boost creativity, or dive into personal reflection. However, this use should always be approached with responsibility and respect for its potency.
 Personalized attention +34 96 206 62 98
Personalized attention +34 96 206 62 98 Free shipping to Iberian Peninsula from 30€
Free shipping to Iberian Peninsula from 30€ 9/10 Rating
9/10 Rating Discreet shipping
Discreet shipping