Today we’re going to talk about cannabis anatomy and how cannabis plants work; regular consumers know all about cannabis but few know how they actually work on the inside. This article will hopefully help you to understand your plant’s phases, and how they turn light, water and gases into energy to grow and flower.
First, we’re going to explain the different parts of the plant to later understand why the plant does certain things like growing out the stems, or why the leaves have a certain amount of points  which people think is either random or down to genetics when it’s actually not.
which people think is either random or down to genetics when it’s actually not.
Your precious cannabis plants form cells that join together and create important plant tissues. These cells reproduce and grow, thus allowing your plants to grow. Some cells reproduce much faster than others; the cells in the stems reproduce slowly, and the fastest reproducing ones are those that are at the tips of the roots and in the new sprouting leaves. Cells reproduce, making plant tissue, and then they absorb water particles and they swell up and grow by expansion. Adult cannabis plants (with a large amount of reproducing cells) in the sun and in good health can grow from 3 to 6cm a day in height and branch length.
 Not all cell tissue has the purpose of growing the plant; other tissues are used to transport nutrients, which are like the veins of the plant. There are tissues that make up the roots, like the plant’s mouth, or the leaves which are like the plant’s lungs as well as many other important organs. When cells are born in these plants they’re kind of like mother cells; they can be used in any tissue and in any part of the plant, and once they’ve found their purpose they’ll stay there until the job is done.
Not all cell tissue has the purpose of growing the plant; other tissues are used to transport nutrients, which are like the veins of the plant. There are tissues that make up the roots, like the plant’s mouth, or the leaves which are like the plant’s lungs as well as many other important organs. When cells are born in these plants they’re kind of like mother cells; they can be used in any tissue and in any part of the plant, and once they’ve found their purpose they’ll stay there until the job is done.
Some of them are in charge of growing the plant, the stems, the leaves and transforming light and CO2 into nutrients for the plant. Other cells are in charge of transporting those nutrients to the parts of the plant that need it the most. Other cells are in charge of creating a sort of skin layer that isolates the rest of the cells to avoid plants dehydrating too fast; these cells open or close depending on the state of the plant in order to let more humidity or heat in.
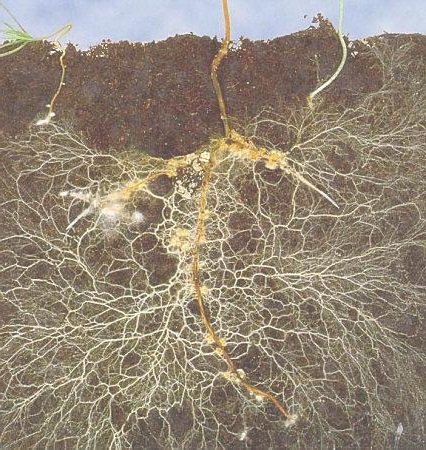 Then, we have the tissue that makes up the roots. Just like the upper side of the plant, the roots grow rather fast every day; the roots are in charge of various functions such as anchoring the plant to the ground so it can put up with the weight of the buds, as well as being in charge of absorbing water and nutrients from the ground; roots are capable of reaching deep levels of ground, growing much larger than the plant in order to ensure its survival.
Then, we have the tissue that makes up the roots. Just like the upper side of the plant, the roots grow rather fast every day; the roots are in charge of various functions such as anchoring the plant to the ground so it can put up with the weight of the buds, as well as being in charge of absorbing water and nutrients from the ground; roots are capable of reaching deep levels of ground, growing much larger than the plant in order to ensure its survival.
When in the process of photosynthesis, plants release water vapor which creates pressure that makes the roots absorb water from the soil. When you water your plants and soak the soil you’re creating another sort of pressure which pushes the water into the roots.
This makes for a perfect balance between ingoing and outgoing water in the plant, allowing it to accelerate many processes and create more cells that do exactly what they’re supposed to do.
 What happens if that balance is broken? If the stoma in the leaves close up (stoma are like doors that allow vapor out) which could happen because the plants are too close to the light or they’re lacking ventilation, then the vapor won’t evaporate but when you water the plants will still be pressured to drink. This means that there will most likely be excess water in the substrate, and due to the plant not being able to take on more water the roots might end up rotting; this will also push the excess water between the cells and the plants will grow fragile, thin and extremely weak.
What happens if that balance is broken? If the stoma in the leaves close up (stoma are like doors that allow vapor out) which could happen because the plants are too close to the light or they’re lacking ventilation, then the vapor won’t evaporate but when you water the plants will still be pressured to drink. This means that there will most likely be excess water in the substrate, and due to the plant not being able to take on more water the roots might end up rotting; this will also push the excess water between the cells and the plants will grow fragile, thin and extremely weak.
The healthier the roots are, the healthier your plant will be in general; if your plant isn’t able to absorb any more water through the roots and it’s also going to evaporate water then it will most definitely dry up and die. The roots need to be white and hairy, as those little hairs are where water is absorbed through; those hairs can burn out and rot, and if this happens your plants will be defenseless and have many health problems. Roots that look brown tend to indicate health issues and problems within the plant.
 The trunk is the exoskeleton of the plant, and it’s in charge of dealing with the weight of the entire plant and allowing water to move freely through the plant, including nutrients.
The trunk is the exoskeleton of the plant, and it’s in charge of dealing with the weight of the entire plant and allowing water to move freely through the plant, including nutrients.
The trunk has two layers with two kinds of tissues; one of them is in charge of transporting water from the roots to the upper parts of the plant. The other kinds of tissues are in charge of moving nutrients around to wherever they’re needed, like sugars produced in the leaves during photosynthesis – unlike the other tissues that bring water from the roots to the top, these tissues can move nutrients to absolutely any part of the plant.
This is why it’s important that your plants grow with a nice strong trunk, guaranteeing that your plant can deal with the heavy weight of buds without bending over or simply breaking in half. A good, strong trunk also ensures optimal nutrient and water transportation around the plant.
To avoid having weak plants indoors then you can simply place a turning fan that blows air on your plants. This air resistance will help your plants grow much stronger with a thicker trunk in order to withstand the wind. Don’t set the air flow too high though, as you don’t want to damage your plants, just give them a little breeze.
 The leaves on cannabis plants are in charge of two things; they contain the cells that move chlorophyll around the plants and that transform sunlight into nutrients for your plant, and they also have stomas on the lower part of the leaves that open and close, allowing CO2 in and water vapor out. Stomas protect plants from dehydration; a leaf that’s in the sun will be much thicker and able to breathe better than leaves in the shade; this means that it produces much more nutrients than leaves in the shade.
The leaves on cannabis plants are in charge of two things; they contain the cells that move chlorophyll around the plants and that transform sunlight into nutrients for your plant, and they also have stomas on the lower part of the leaves that open and close, allowing CO2 in and water vapor out. Stomas protect plants from dehydration; a leaf that’s in the sun will be much thicker and able to breathe better than leaves in the shade; this means that it produces much more nutrients than leaves in the shade.
This doesn’t mean that leaves in the shade are absolutely useless; they just reach their maximum nutrient potential much earlier than one that’s in the sun. Leaves in the shade still give your plants energy, so don’t even think about removing them! When they begin growing they start off with three tips per leaf and as they grow the leaves grow more tips; the healthiest plants and plants that breathe the most can reach up to 13 tips whereas the average amount is around 7 to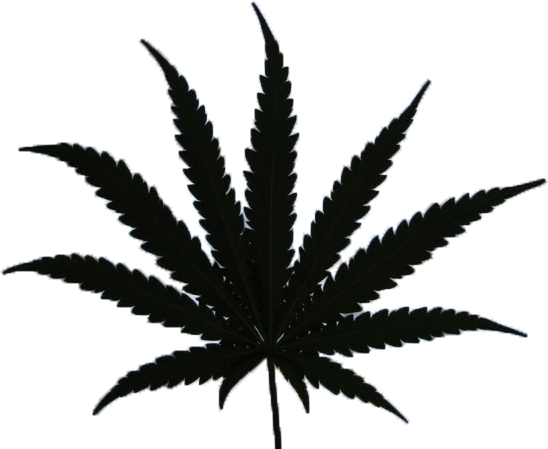  9. By tips we mean leaflets that grow from the central stem, which is why they’re called compound leaves, and they always tend to be uneven in number.
9. By tips we mean leaflets that grow from the central stem, which is why they’re called compound leaves, and they always tend to be uneven in number.
Lastly, we’re going to talk about our favorite part of the plant and the main reason why many people grow their own cannabis; the flowers. Flowers are in charge of the plant’s reproduction; there are male and female plants, and the female plants are the ones that give the most amount of cannabinoids in their flowers, the most desired one being THC. Female plants possess what are known as calyxes, and the male plants are in charge of pollinating those calyxes. When male flowers are mature enough, they release the pollen which then flows through the air to fall onto the female flower, and inside the calyx seeds begin to grow which then, in nature, fall to the ground to grow as a new plant, ensuring the survival of the species.
When the seeds begin to form, plants will have reached their objective which is essentially to reproduce, rather than get people high; plants concentrate all of their energy on making seeds. If you have a plant that isn’t pollinated, it will keep growing new calyxes in a desperate attempt to catch some pollen and reproduce; it also begins producing much more resin to make sure that any possible pollen sticks to the flowers. The resin is where most of the cannabinoids lie in a plant, so if you want a smokeable, seed-free plant we recommend protecting them from being pollinated by getting rid of any male plants from your grow if you want some medicinal or recreational flowers.
This is more or less how cannabis plants behave on the inside explained in simple terms. Knowing how it works on the inside will help you figure out what’s happening on the outside. Keep in mind that pH, EC, temperature and humidity are extremely important for all of these factors.
Author: Javier Chinesta
Translation: Ciara Murphy







